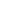
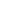
Bitumen tank container
Bitumen tank container
Shell made from carbon steel
Capacity of 20000 liters up to 25000 liters
MAWP of 1.75 bar
Low hazardous liquids
Availability stock 20 feet or 30 feet sizesAlso Swap-bodies 7.15m (30,000 litres) and 7.82 (35,000 litres)
Heating by direct flame, hot oil or electric heating
Design temp. 230 C
3" and 4" bottom discharge
Heavy insulation 50mm
Approval by indipendent survey companies
Asphalt, also known as bitumen, is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product; it is a substance classed as a pitch. Until the 20th century, the term asphaltum was also used.
The primary use of asphalt/bitumen is in road construction, where it is used as the glue or binder mixed with aggregate particles to create asphalt concrete. Its other main uses are for bituminous waterproofing products, including production of roofing felt and for sealing flat roofs.
The terms asphalt and bitumen are often used interchangeably to mean both natural and manufactured forms of the substance. In American English, asphalt (or asphalt cement) is the carefully refined residue from the distillation process of selected crude oils. Outside the United States, the product is often called bitumen. Geological terminology often prefers the term bitumen. Common usage often refers to various forms of asphalt/bitumen as "tar", such as at the La Brea Tar Pits. Another term, mostly archaic, refers to asphalt/bitumen as "pitch". The pitch used in this mixture is sometimes found in natural deposits but usually made by the distillation of crude oil.
Naturally occurring asphalt/bitumen is sometimes specified by the term "crude bitumen"; its viscosity is similar to that of cold molsses whilst the material obtained from the fractional distillation of crude oil [boiling at 525 °C (977 °F)] is sometimes referred to as "refined bitumen".